|
Molecular characterization and diagnosis of microorganisms viruses, and oncogenes
| | |
| 
Followings are completed or pending research projects which I have been involved in along with corresponding data:
1. Optimization of Leishmania spp. detection through PCR in order to design a diagnostic kit. 2003.
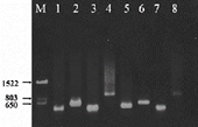 PCR analyses using 4 pairs of primers were used in diagnosis of 2 isolates of Leishmania infantum shown on lanes 1-4 and 5-8 respectively. Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products as stained with EtBr, along with molecular weight marker (lane “M”) and corresponding fragment sizes are shown on the left-hand side. PCR analyses using 4 pairs of primers were used in diagnosis of 2 isolates of Leishmania infantum shown on lanes 1-4 and 5-8 respectively. Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products as stained with EtBr, along with molecular weight marker (lane “M”) and corresponding fragment sizes are shown on the left-hand side.
|
| | |
|
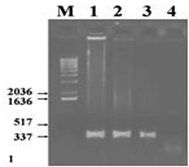
Agarose gel analysis demonstrating the results of PCR on 2 clinical samples obtained from dog spleen (lane 2) and hamster spleen (lane 3). A pure culture of Leishmania infantum MON 1 was used as positive control (lane 1) and a no template reaction used as negative control (lane 4). Numbers on the left correspond with fragment length in bp.
| 
|
| | |
| 2. Diagnosis and detection of Enterococcus faecalis in necrotic dental root canals through polymerase chain reactions (PCR) and investigating its association with clinical symptoms. 2004 Gradient multiplex-PCR on 1% agarose gel stained with EtBr, along with molecular weight marker (lane “M”) and corresponding fragment sizes shown on the left-hand side. PCR was conducted over a broad range of annealing temperature from 50 to 60 °C (lanes 1 through 6). Numbers on the right-hand side correspond to the fragment sizes of PCR products from E. faecalis. | 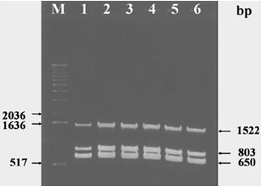
|
| | |
| Agarose gel electrophoresis of multiplex PCR products from clinical samples taken from necrotic root canals. Lane “M” represent the molecular weight marker, with corresponding fragment sizes on the left-hand side. Lanes 1, 2, 7, and 8 represent E. faecalis infection. In lanes 4 and 5, amplification of the 16S rRNA gene (internal control) detects bacteria other than E. faecalis. No amplification is seen in lanes 3 and 6 for samples grown in the presence of 6.5% NaCl. Lane 9 is a PCR negative control. Numbers on the right-hand side of the figure correspond to the fragment sizes of the PCR products. | 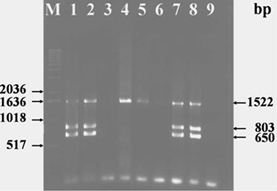 |
| | |
| 3. Diagnosis, detection, and subspecies identification of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in patients with Localized Aggressive Periodontitis through polymerase chain reactions (PCR). 2004 Four positively identified serotypes of Actiobacillus actiomycetemcomitans are diagnosed specifically by multiplex PCR composed of 5 pairs of primers. PCR products were analyzed on 1% agarose gel stained with EtBr, along with molecular weight marker (lane “M”) and corresponding fragment sizes shown on the left-hand side. | 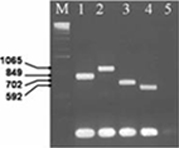
|
| 4. Cloning and expression of gene K26 from Leishmania infantum and assessing its potential in diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis through ELISA. 2004.
5. Investigating the genetic diversity of wild species of barley, Hordeum spp., in East Azarbaijan through PCR and RFLP. 2005. 6. Genetic studies of pathogenic species of Leishmania in Iran through cloning and nucleotide sequence determination of mitochondrial minicircle DNA in order to improve the molecular diagnosis through polymerase chain reactions (PCR). 2005. 7. Designing, establishing, and optimizing procedure for diagnosis and detection of Helicobacter pylori through polymerase chain reaction (PCR). 2005. |
| ....... |
|
PCR analyses using 4 pairs of primers were used in diagnosis of a positively identified isolate of Helicobacter pylori. PCR products were analyzed on 1% agarose gel stained with EtBr, along with molecular weight marker (lane “M”) and corresponding fragment sizes shown on the both sides. | 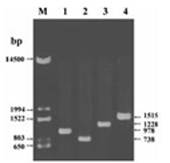 | |
| 8. Diagnosis and detection of Helicobacter pylori in dental plaques through polymerase chain reaction (PCR). 2005.
9. Cytogenetics and molecular genetic studies in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) before and after treatment. 2005.
10. Detection of CEA-mRNA through RT-PCR in peripheral blood obtained from 50 colorectal cancer patients and determining its association with tumor markers of blood serum and disease stage. 2005.
11. Application of phage display method in development of new peptide carriers and monoclonal antibodies. 2005.
|